Quantum computing is one of the most exciting fields of study in today's technology; it involves using the quantum state of subatomic particles to process information much faster than conventional computers.
In recent years, quantum computing has gained significant attention from researchers, governments, and businesses as it has the potential to revolutionize almost all aspects of our lives, including healthcare, finance, cybersecurity, and more. However, for most people, the idea of quantum computing is still mysterious and abstract.
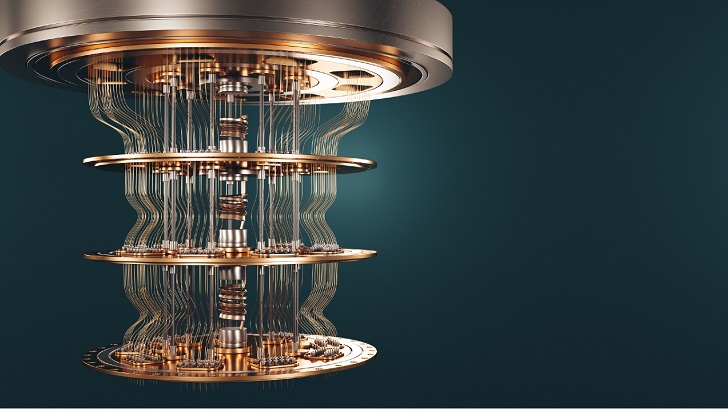
Stephen Shankland/ CNET | Quantum computers are elegant machines, smaller and requiring less energy than supercomputers
Understanding Quantum Computing
One of the fundamental principles of classical computing is that information is stored in bits, either a 0 or 1 value. In contrast, quantum computing relies on qubits, storing data in two separate quantum states. These quantum states exist in a fragile balance easily distributed by external interference.
The unique properties of qubits mean that a quantum computer can execute specific calculations that a classical computer cannot. For instance, it can handle large volumes of data simultaneously and perform sophisticated computations that can solve complex problems in a fraction of the time it would take a traditional computer.
Recent Advancement
Quantum computing has continued to advance with the advent of more advanced computer hardware and novel algorithms. Several tech giants, such as IBM, Google, and Microsoft, have made significant investments in quantum computing and are all making strides in the field. In 2022, Google announced that it had achieved quantum supremacy by demonstrating the ability of its 53-qubit Sycamore processor to perform a specific calculation in just 200 seconds.
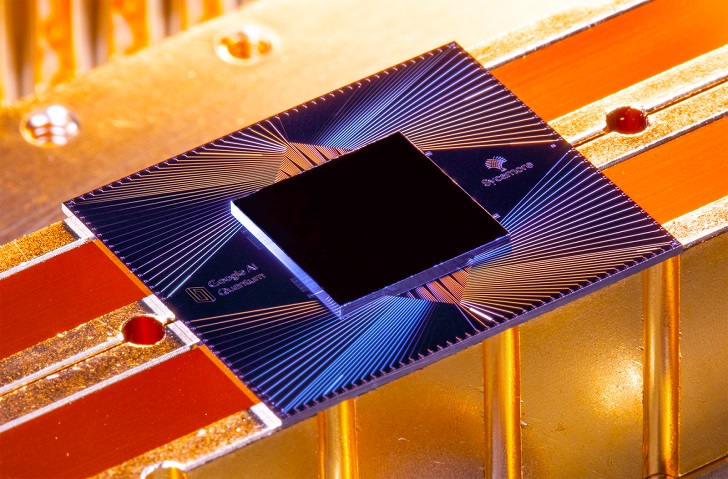
Samiha Tashin/ Q-munity | Google Sycamore is a quantum computer developed by Google AI Quantum
To put things in perspective, this calculation would have taken the world's most powerful classical supercomputer 10,000 years to solve. This achievement has significant implications for the future of computing and reinforces the hype surrounding the capabilities of quantum computing. But that's not all; quantum computing is anticipated to disrupt several sectors traditionally reliant on classical computing.
For instance, financial institutions could use quantum computing to optimize portfolios to reduce risk and enhance profitability. In healthcare, scientists could analyze vast amounts of genomic data faster and more efficiently, thereby increasing drug development. In cybersecurity, quantum computing can break traditional encryption methods, and technologists must develop new protocols to secure sensitive data.
Rising Concerns
However, the development of quantum computing also raises some concerns, particularly regarding security. For instance, quantum computing algorithms could be used to break existing encryption models, rendering them vulnerable to outside attacks.
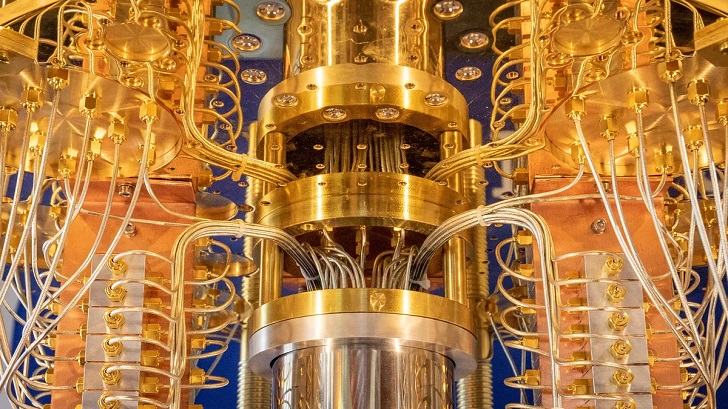

Stephen Shankland/ CNET | Quantum computers have the potential to solve certain problems exponentially faster than classical computers
The issue is that quantum computers can hack into encrypted data; instead, there is no known way to fix it. Several businesses, governments, and technological institutions have started investing in post-quantum cryptography algorithms and methods to counter such threats.
Quantum Computing Investment
Investment in quantum computing is significant as the technology plays catch-up with its classical counterpart. Quantum computing firms have garnered over $680 million in funding, which is expected to rise even further. All significant technology companies are investing in quantum computing and their surrounding ecosystem.
This investment in quantum computing shows enormous potential in the field, and while not mainstream yet, it is set to grow. With time, we expect quantum computing to become pervasive in systems, and more affordable and refined versions will become available.



